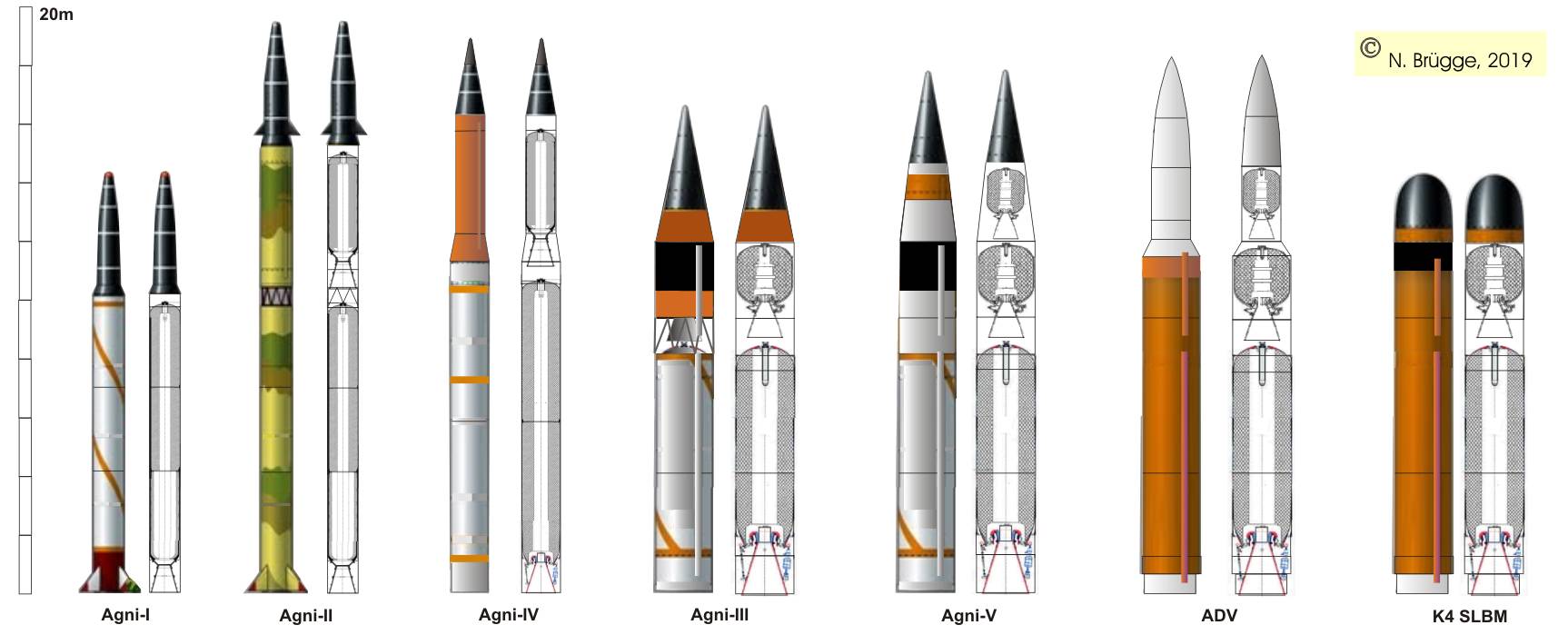
India;s solidfuel missile "Agni"
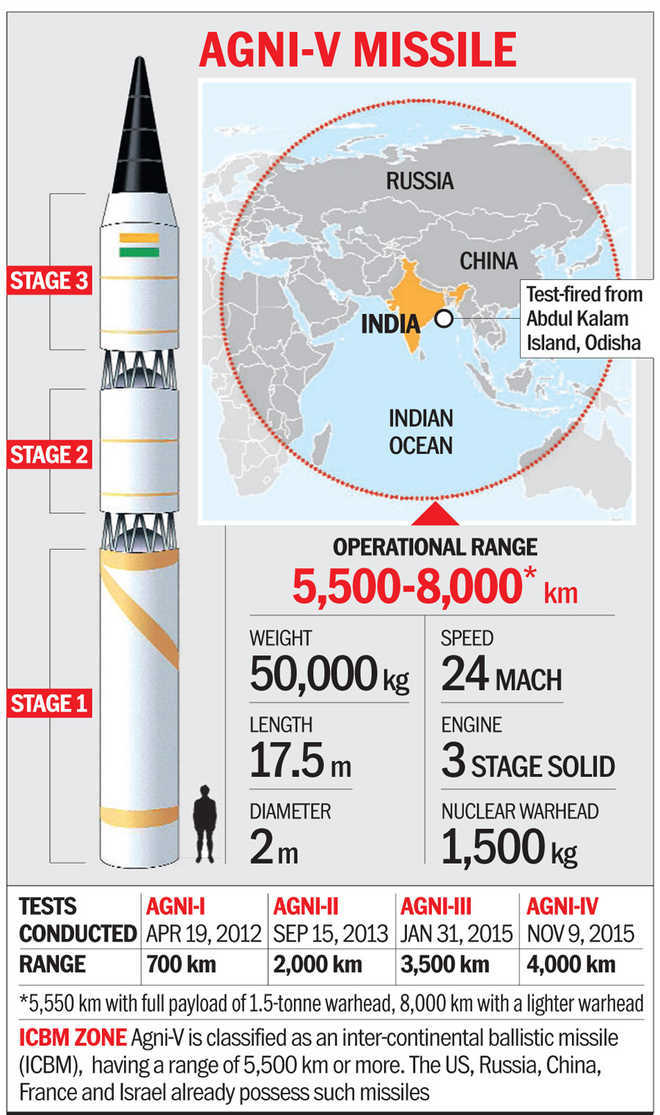
Agni-V is a three-stage, solid propellant, and intercontinental ballistic surface-to-surface missile. It is about 17-meter long and weighs over 50 tonnes. With a massive range of 5,500 to 5,800 kilometers, it is nuclear-capable, with a payload capacity of 1,500 kg of a high-explosive warhead.

Agni Prime DRDO's latest ballistic missile is short in size yet powerful. See pics Mint
The Agni-IV is an Indian solid-fueled intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) with a range of up to 4,000 km. The two-stage missile, previously named Agni-II Prime, is a derivative of the Agni-II MRBM with extended range. India has flight tested the Agni-IV eight times since its first test in 2010. Agni-IV Development India's Defence Research and.

Agni5 3D model by JamesMartinCNS [e4c2415] Sketchfab
Agni-I (Agni "Fire") is a medium-range ballistic missile that was developed by DRDO of India in the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program.It is a single-stage missile that was developed after the Kargil War to fill the gap between the 250 km (160-mile) range of the Prithvi-II missile and the 2,500 km (1,600-mile) range of the Agni-II.It was first launched from a road mobile launcher at.

How APJ Abdul Kalam Became the 'Missile Man of India' YouTube
The Agni-I is an Indian short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) with a range of 700 km. The Indian Army's Strategic Forces Command first deployed the nuclear-capable, road-mobile missile in 2007. Agni-I Development The Agni-I originated from India's 1983 Integrated Guided Missile Development Program, which also developed the Prithvi, Nag, Akash, and Trishul missiles. India's Defence Research.

Agni Missile
Agni-V (Fire) is a land based nuclear capable intercontinental ballistic missile ICBM developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India. The missile has a range of more than 7,000 kilometers. Chinese researchers allege that the missile has the range of 8,000 kilometers. It is a three-stage, road-mobile, canisterised, solid-fueled intercontinental ballistic missile.

AgniII Missile Threat
BHUBANESWAR: Riding high on the success of 30 missions in last three months, India plans to deploy its longest range most potent nuclear-capable ballistic missile Agni-V this year.

Misil PNG
The two-stage, solid-fuel, road-mobile Agni-I missile became operational in 2007, three years after its induction into the armed forces.. with no successor or next series on the horizon or even on the drawing board" (Gupta 2018), India apparently has also begun development of a true ICBM, known as Agni-VI. Official data is scarce, but an.

AgniP Missile UPSC Notes
Agni-P or Agni-Prime (Agnī "Fire") is a medium-range ballistic missile being developed by India's Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) as a successor for Agni-I and Agni-II missiles in the operational service of Strategic Forces Command with significant upgrades in the form of composite motor casing, maneuverable reentry vehicle (MaRV) along with improved propellants.

February 2010 Sushantskoltey's Blog Atombombe, Rakete, Lebenslanges lernen
May 4, 2021 The Agni-III is an Indian intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) with a range of 3,000 - 3,500 km. It entered service with India's Strategic Forces Command in 2011, serving alongside the Agni-II as a nuclear delivery system. 1 Agni-III at a Glance Originated from India Class Intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) Possessed by

India Successfully Conducts Second Agni Prime Ballistic Missile Test
2023-09-26. In the past few months, interest in the Agni 6 missile has shot up after it was revealed that a honey-trapped Defence Research and Development Organisation scientist had divulged the Agni 6 missile launcher details to Pakistanis. Then, this month, DRDO released an image depicting the missile during a Defence Expo in Chennai.
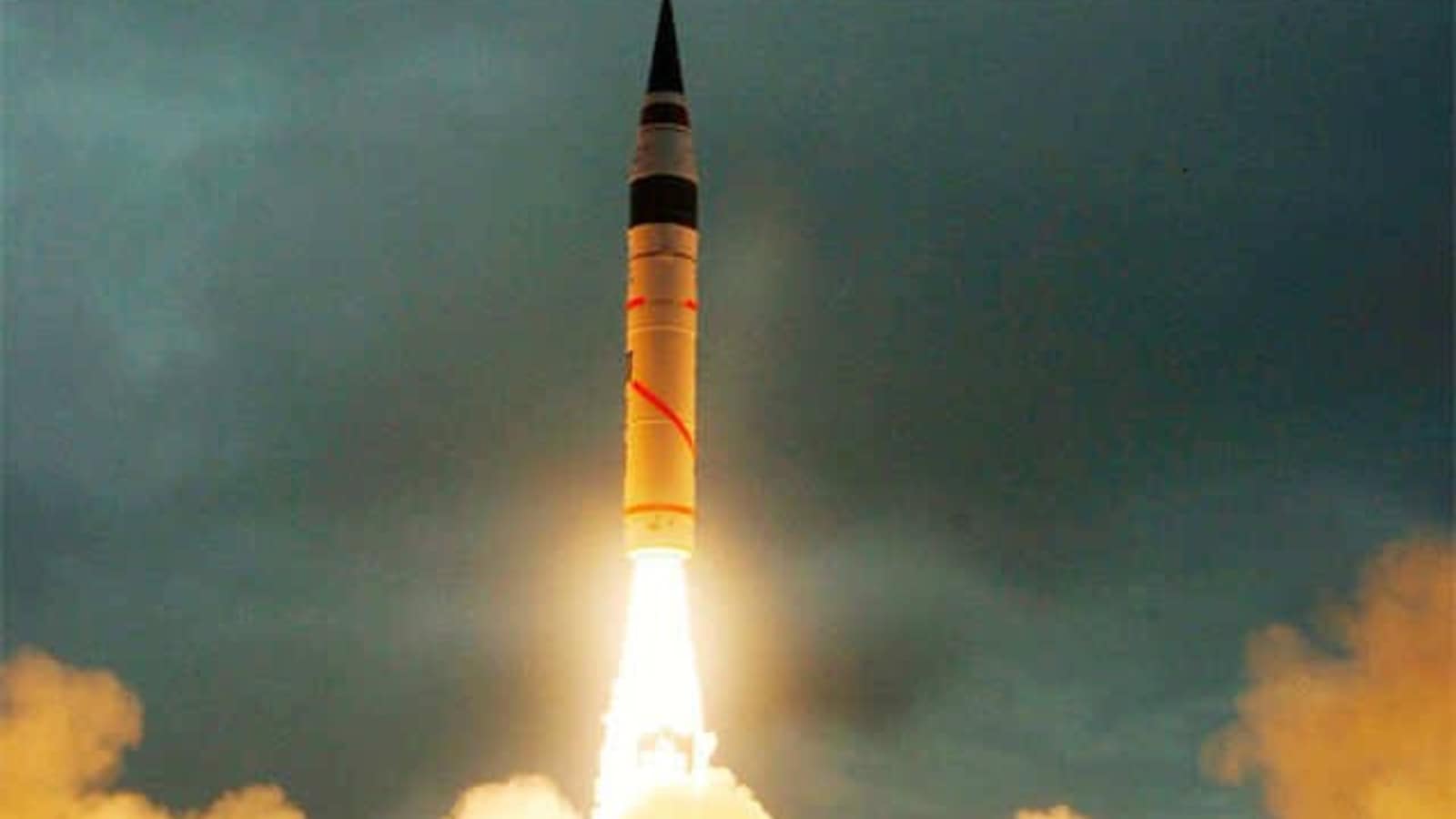

Strategic Forces Command conducts Agni V trial, hits target 5000 km away Latest News India
Agni-5 missile test: What was the latest test for? Agni-5 has been successfully tested multiple times since 2012. Defence Ministry sources said the latest test was carried out primarily to validate various new technologies on board the missile. The flight performance of the missile was tracked and monitored by radars, range stations and.
India testfires AgniV Ballistic Missile amid LAC heat Civilsdaily
The Agni-V is the fifth variant of India's long-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile. India has a long history with the Agni series of missiles, dating back to 1989. At the time, India had test-fired Agni-I, an Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile, with a range of around 1,000 km.
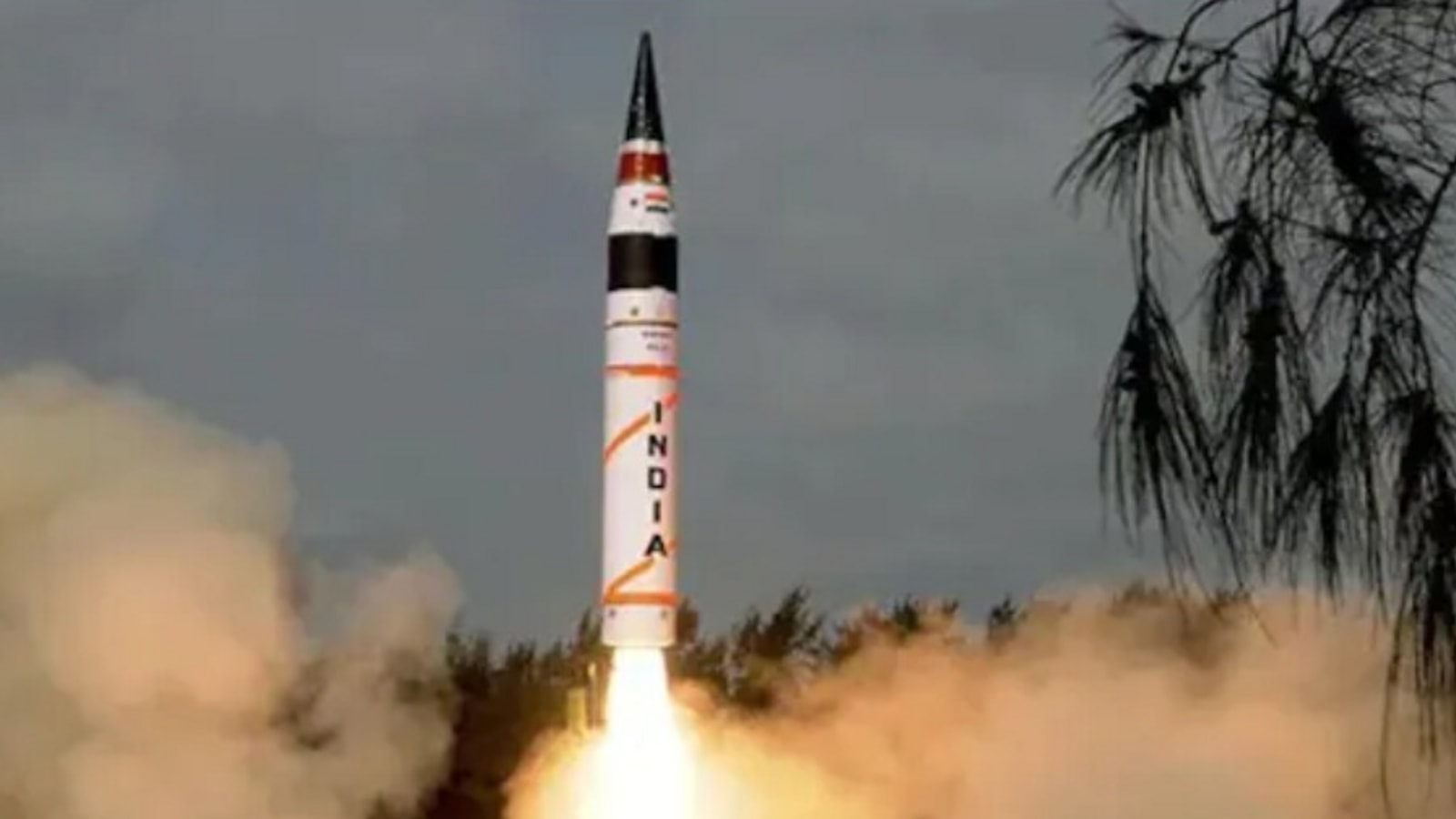

Has the range of Agni V missile been increased? TrendRadars India
A successful launch of the Surface to Surface Ballistic Missile, Agni-5, was carried out on October 27, 2021 at approximately 1950 hrs from APJ Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha. The missile, which uses a three-stage solid fuelled engine, is capable of striking targets at ranges up to 5,000 kilometres with a very high degree of accuracy. The.

AgniV Missile Threat
Unlike other Indian land-based ballistic missiles, the Agni-V is carried in a sealed canister on the launcher. The four most recent Agni-V tests took place from canisters.. with no successor or next series on the horizon or even on the drawing board" (Gupta Citation 2018), India apparently has also begun development of a true ICBM,.

K15 Shaurya Page 6 Indian Defence Forum
Agni-1 is a single stage missile, it is essentially an Agni-2 without its second stage. The first stage is made from maraging steel and it uses fins for control. Its first stage diameter is 1m and its length is around 15m. It has a reported range of 700km which makes it a missile primarily focused towards Pakistan.
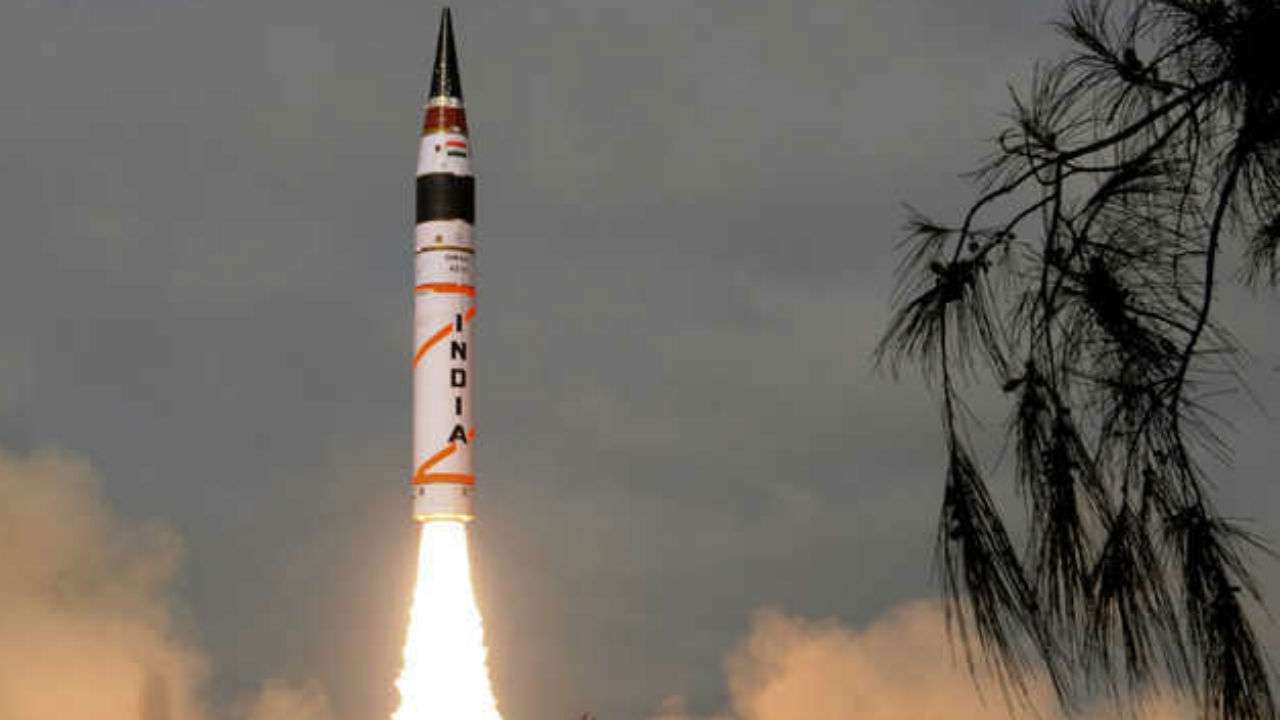

Agni II Launch India successfully test fires nuclear missile off Odisha Coast
The Agni-V is an Indian intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) with a range of over 5,000 km. It is an evolution of the Agni-III IRBM, featuring similar first- and second-stage motors with an added third stage. India first tested the solid-fueled missile in 2012, conducting subsequent tests in 2013, 2015, 2016, and 2018. Unlike earlier missiles,.